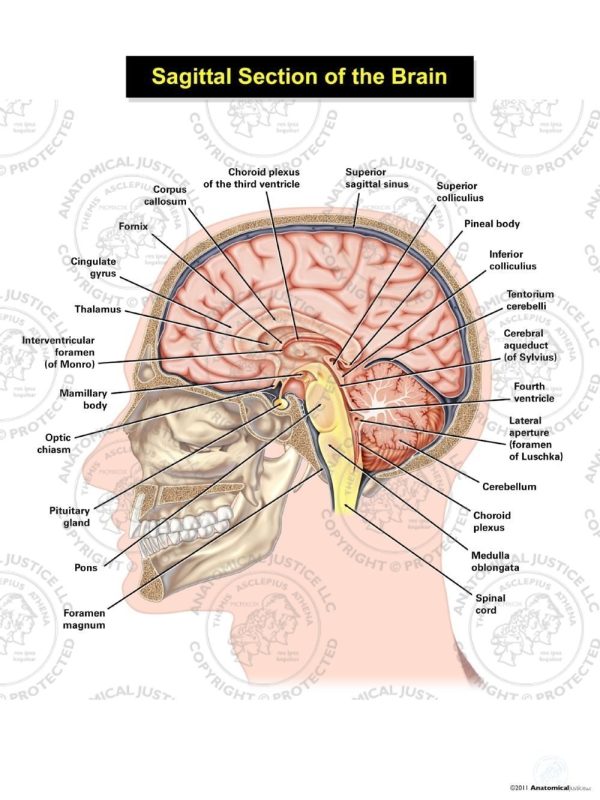
Sagittal Section of the Brain Illustration Anatomical Justice
The sagittal suture extends posteriorly from the coronal suture, running along the midline at the top of the skull in the sagittal plane of section (see Figure 7.9). It unites the right and left parietal bones. On the posterior skull, the sagittal suture terminates by joining the lambdoid suture.
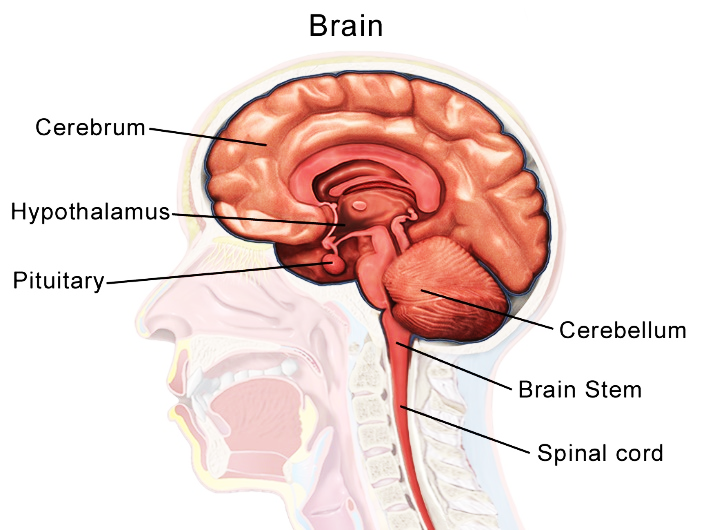
Draw a neat labelled diagram of the sagittal section of the brain.
Introduction Go to the Interactive Neuroanatomy Atlas for an interactive view of myelin-stained sections of the CNS The atlas of myelin-stained sections through the central nervous system is in three planes: transverse, horizontal, and sagittal. (See Figure 1-17 for schematic views of these planes of sections.)
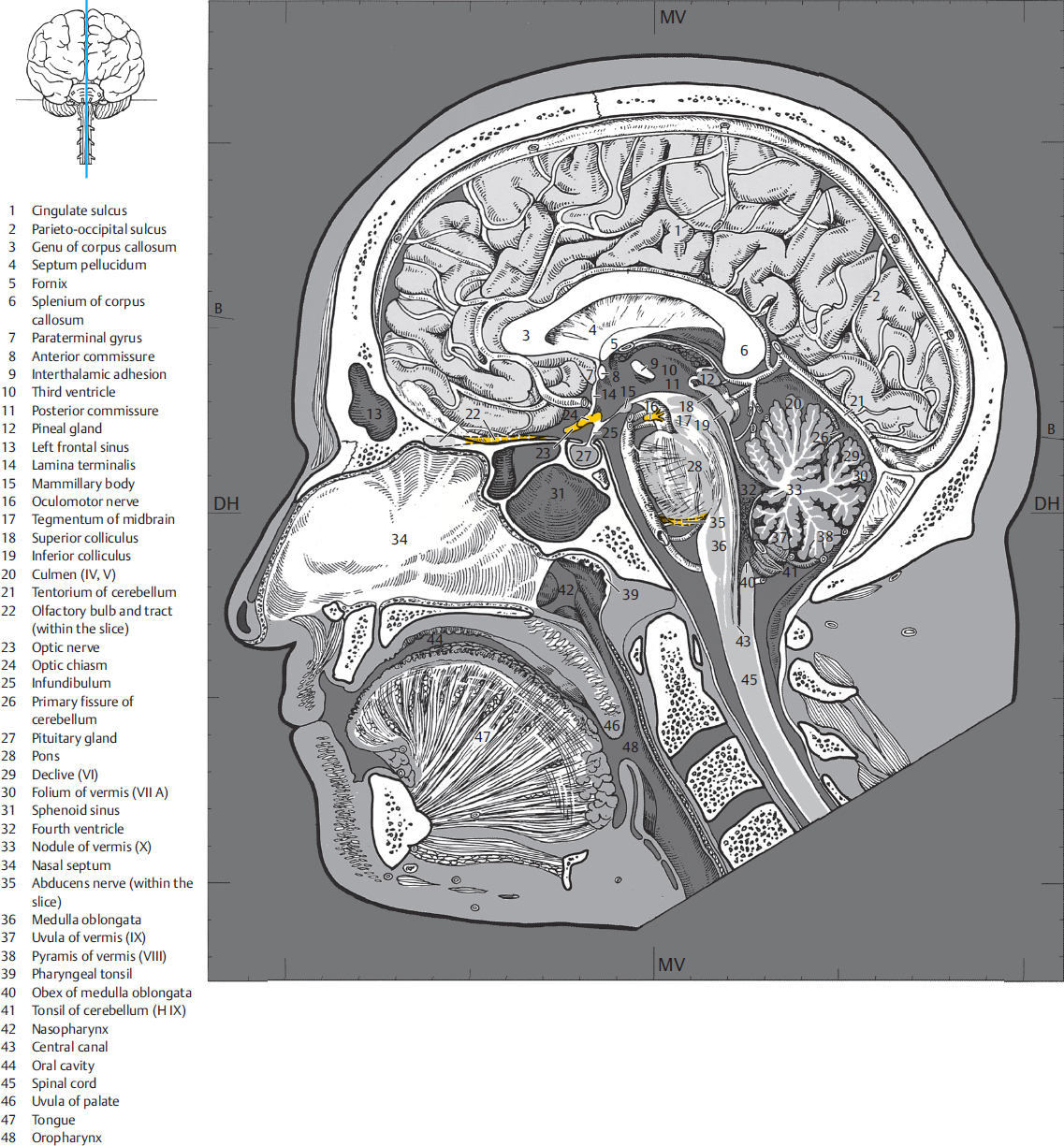
4 Sagittal Sections Radiology Key
Definition Stalklike portion of the brain that connects the cerebral hemispheres with the spinal cord; consists of the pons, medulla oblongata, midbrain, and interbrain Location Term Spinal Cord Definition Caudal continuation of the medulla oblongata Location Term Medulla Oblongata Definition
[Solved] Label the sagittal section of the brain and spinal cord. Pons
Cerebellum Forebrain (diencephalon, telencephalon) The craniocervical junction continues into the spinal cord. The typical shape of the corpus callosum and its lesions, as well as aplasia or atrophy thereof, are visualized in the median plane.

4 Sagittal Sections Radiology Key
The 22nd bone is the mandible (lower jaw), which is the only moveable bone of the skull. Figure 7.3.1 - Parts of the Skull: The skull consists of the rounded cranium that houses the brain and the facial bones that form the upper and lower jaws, nose, orbits, and other facial structures.

Human Brain Sagittal Section With Labels Ilustração Getty Images
The frontal or coronal plane is a vertical plane in a medial to lateral direction, dividing objects into front and back pieces. The sagittal plane is also a vertical plane but in a rostral-caudal direction, meaning it divides objects into right and left regions. Finally, the horizontal plane divides objects into top and bottom regions. Figure 16.2.

Midsagittal (side) view of the human brain. The tentorium cerebelli is
In clinical practice, the nervous system is usually visualised in sections that cut through one of the three main orthogonal planes: sagittal, coronal or horizontal .Each of these planes provides the clinician with information that allows the precise localisation and description of lesions (i.e. tumours ) within the neuroaxis. As such, being able to identify anatomical structures of the brain.
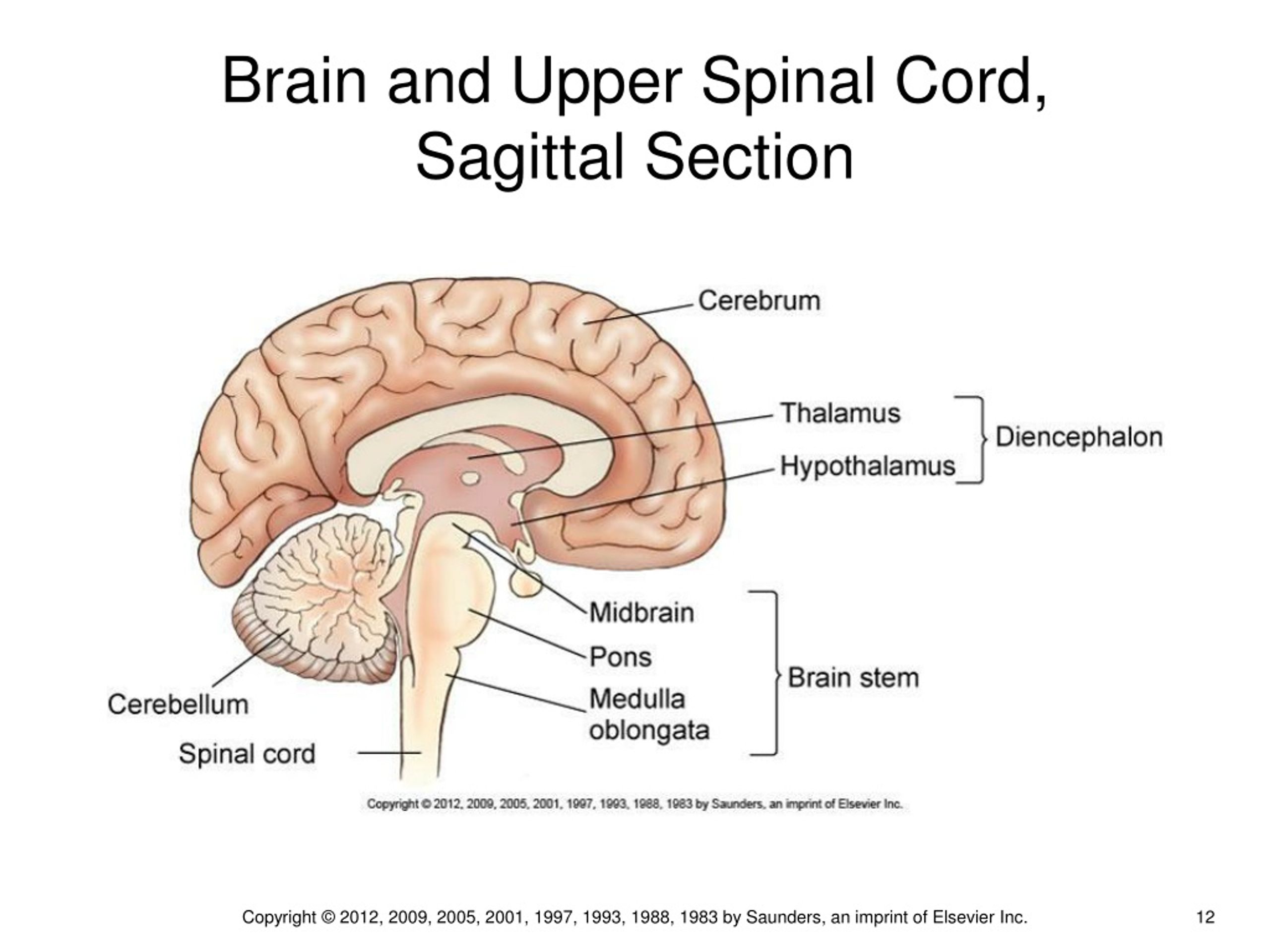
PPT Chapter 15 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID241128
Midsagittal section of the brain Author: Sara Ferreira MD • Reviewer: Roberto Grujičić MD Last reviewed: August 08, 2023 Reading time: 12 minutes Recommended video: Medial view of the brain [38:16] Structures seen on the medial view of the brain. The images show a midsagittal section of the brain. Cerebrum 1/9

Sagittal Section of the Brain Stock Vector Illustration of sagittal
Most electromagnetic imaging techniques produce images of the brain in the coronal, horizontal (axial) and sagittal planes. The representative sections are transverse sections through the spinal cord and brain stem and coronal sections through the telencephalon and diencephalon (Figure 1.17).

Sagittal section of brain and spinal cord Diagram Quizlet
A mid-sagittal section slices the brain through the longitudinal fissure and separates the right hemisphere from the left. It also reveals more structures. In a mid-sagittal view, all four cortical lobes are visible.. medulla, and spinal cord are seen caudal to the cerebrum, but in this view, the midbrain, which is made up of two regions.
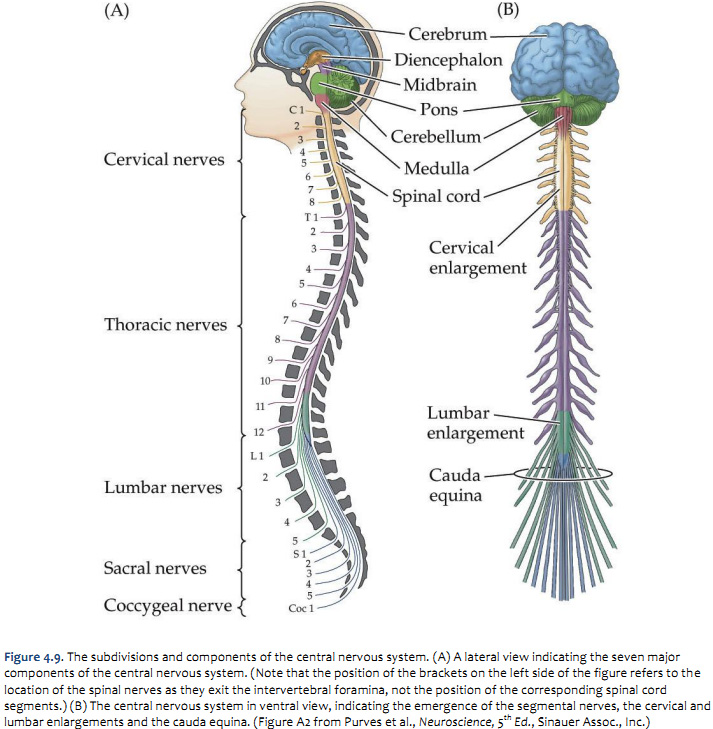
Duke Neurosciences Lab 2 Spinal Cord & Brainstem Surface and
Cerebral Cortex The cerebrum is covered by a continuous layer of gray matter that wraps around either side of the forebrain—the cerebral cortex. This thin, extensive region of wrinkled gray matter is responsible for the higher functions of the nervous system.
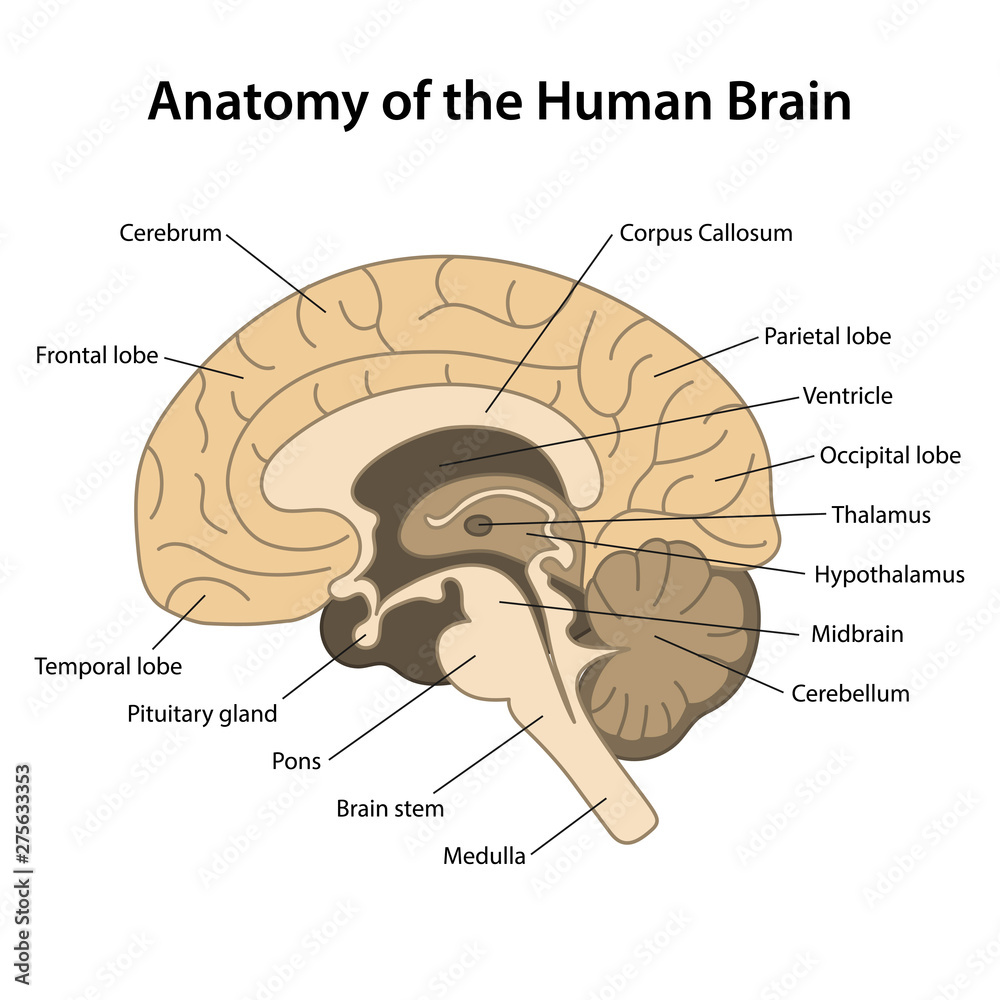
Anatomy of the human brain.Sagittal cut. Structure of the human brain
Sagittal Brain and Spinal Cord Label the sagittal section of the brain and spinal cord. Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Cerebrum Cerebellum Thalamus Medulla oblongata Pons Spinal cord Midbrain O Grow Hal Education This problem has been solved! You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer

Sagital section of the human brain with regions and labels Stock Photo
The spinal cord, which is part of the central nervous system but not part of the brain, is responsible for receiving sensory information from the body and sending motor information to the body. Involuntary motor reflexes are also a function of the spinal cord, indicating that the spinal cord can process information independently from the brain.
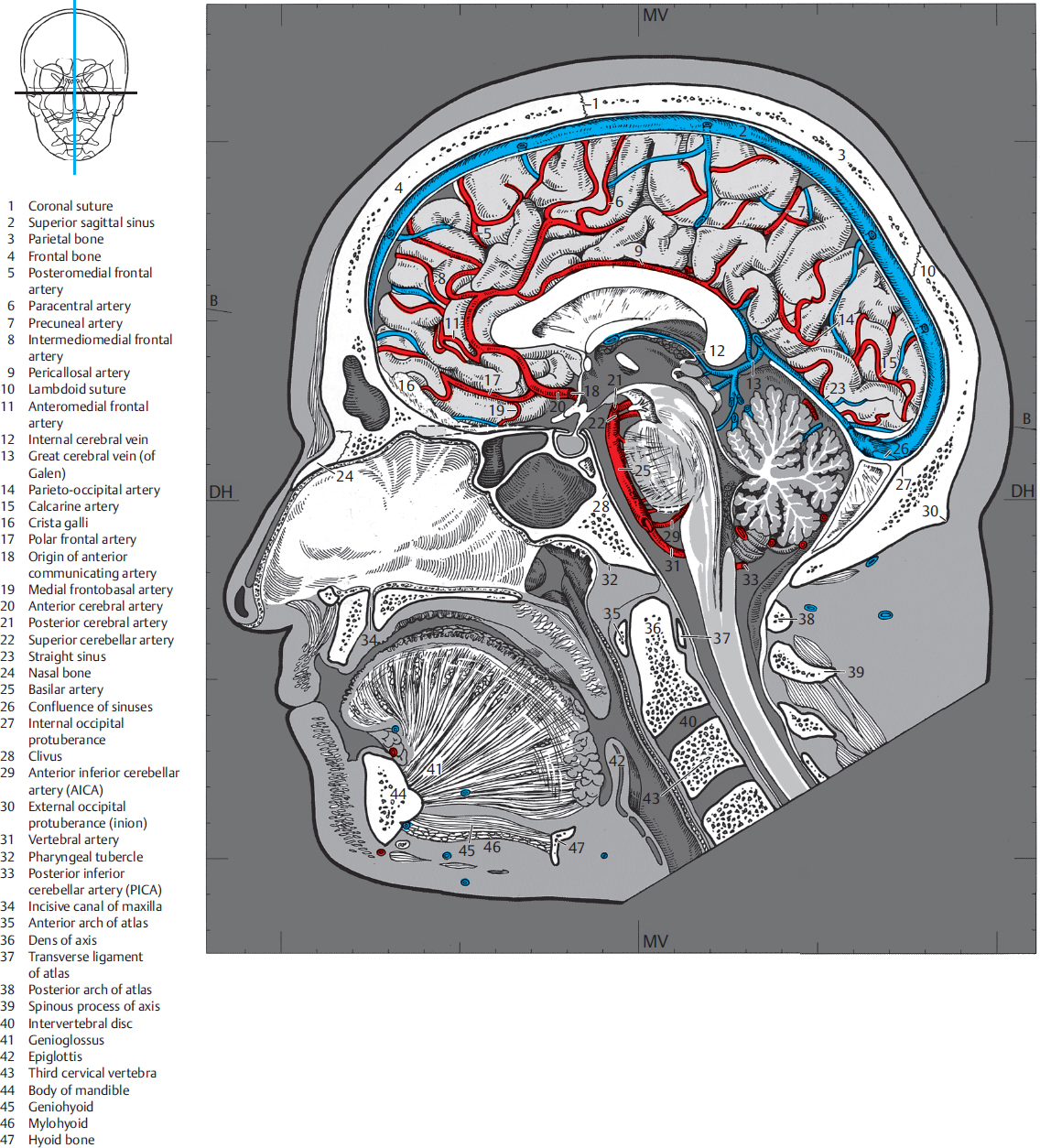
4 Sagittal Sections Radiology Key
Lab 3 Protocols Spinal Cord Learning objective: to recognize the principal features of the spinal cord, including the longitudinal organization of spinal segments and internal distinctions among levels. Specimens: one spinal cord specimen available for demonstration purposes Activities:

Diagram Of The Sagittal View Of The Human Brain koibana.info Human
The arterial supply of the spinal cord. The arterial blood that supplies the spinal cord comes from two sources: the vertebral arteries and segmental arteries that arise from branches of the aorta. These arteries join the anterior and posterior spinal arteries as illustrated in Figure 2.16 and 2.17 (see also Netter 164, 165A, 165B). It is.

Download HD Sagittal View Of The Human Brain Labeled Sagittal Brain
The dura mater: This is the thick, outmost layer located directly under the skull and vertebral column.; The arachnoid mater: This is a thin layer of web-like connective tissue.Under this layer is cerebrospinal fluid that helps cushion the brain and spinal cord. The pia mater: This layer contains veins and arteries and is found directly atop the brain and spinal cord.